
- Tigervnc install ubuntu how to#
- Tigervnc install ubuntu update#
- Tigervnc install ubuntu software#
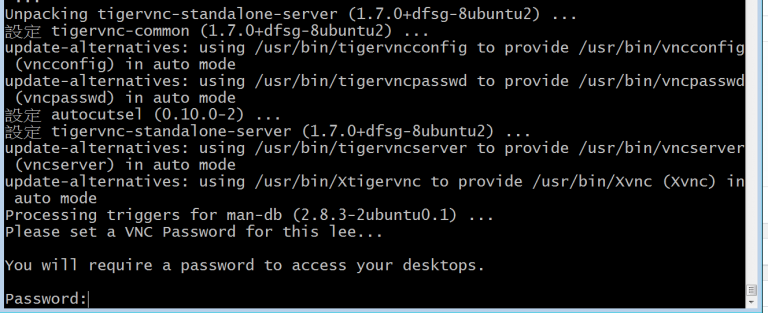
- Tigervnc install ubuntu password#
Next, we need to configure the DE to work with the VNC server.
Tigervnc install ubuntu password#
Then set a view-only password if you wish, as follows. This action will create the initial configuration stored in the $HOME/.vnc directory and it will also prompt you to set up a login password.Įnter a password (which must be at least six characters length) and confirm/verify it. Now start the VNC server by running the vncserver command as a normal user. $ sudo apt install tigervnc-standalone-server tigervnc-common tigervnc-xorg-extension tigervnc-viewer To install TigerVNC server and other associated packages in Ubuntu, run the following command. Tigervnc-server is a high-speed, multi-platform VNC program which runs an Xvnc server and starts parallel sessions of Gnome or other Desktop Environment on the VNC desktop. $ sudo apt-get install kubuntu-desktop #KDE $ sudo apt install ubuntu-gnome-desktop #Ubuntu Gnome (Official flavor) $ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop #Default Ubuntu desktop For the purpose of this article, we will install Ubuntu Gnome (Official flavor). You can install the DE of your choice by running the appropriate commands below. Testing Environment VNC Server: 192.168.56.108Īs I said, VNC is a desktop-sharing system, so you need to have a desktop environment installed on your Ubuntu server.
Tigervnc install ubuntu how to#
In this article, we will explain how to install and configure a VNC Server on a Ubuntu 18.04 Desktop edition via tigervnc-server program. The second GPU is specified as: $ vglrun -display :0.Virtual Network Computing ( VNC) is a widely used graphical desktop-sharing system that allows user accounts to remotely connect and control the desktop interface of one computer from another computer or mobile device. The first GPU is specified as: $ vglrun -display :0.0 glxgears In order to use a GPU other than the default (for example, if the node has multiple GPUs), the user needs to specify its index. To use the GPU inside VNC, the user needs to run the application using the form: $ vglrun APP # chroot /cm/images/default-image systemctl enable rvice Make changes permanentĬopy the nf file back to the image to make sure parameters persists across reboots and enable systemd unit in the image: # scp node003:/etc/X11/nf /cm/images/default-image/etc/X11/ Start and enable the xinit service # systemctl enable rvice Press Ctrl-C to stop.Įrrors will be written in /var/log/Xorg.0.log file 9. If no errors occurred, the command above should stay running. The Section “Files” must be removed from the /etc/X11/nf file # sed -i -e '/Section "Files"/,/EndSection/d' /etc/X11/nf 8. Where PCI:0:7:0 is an address of the GPU acquired on the previous step. UUID : GPU-c621812a-c0e1-dfdd-bc4d-9c65264d6956Ĭreate an /etc/X11/nf file with the following command: # nvidia-xconfig -a -allow-empty-initial-configuration -busid PCI:0:7:0 -no-connected-monitor To do that, the following command can be executed on a node with an NVIDIA GPU: # module load shared cuda10.2/toolkitįetch information about the PCI address of the GPU: # nvidia-xconfig -query-gpu-info
On a target node we need to generate a config for the nf file of the X server. | GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. Reboot the target node (the node which will host the X applications) and make sure GPU is visible: # module load shared cuda10.2/toolkit
Tigervnc install ubuntu update#
Install the cuda toolkit # yum install cuda10.2-toolkitįor Ubuntu 18: # apt update & apt install cuda10.2-toolkit 5. O $/etc/systemd/system/rviceĮxecStart=/usr/bin/xinit - /usr/bin/X -nolisten tcpĤ. Note: for RHEL8/Centos8 the VirtualGL repository must be configured first # wget \
Tigervnc install ubuntu software#
Install VirtualGL packagesįor the RHEL and CentOS distributions, update the software image with the following packages: # yum install \ Preparationĭefine image name for package installation and modifications: # export $IMAGE_PATH="/cm/images/default-image" 1. The display can then be seen on a VNC client somewhere else, such as Jupyter VNC session. The following steps can be followed to enable direct rendering from an x-client (glxgears or similar) running on a headless node, using VNC with the headless X-server display.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
